
#Treatment for pulmonary barotrauma skin
In addition to sinuses, lungs and the GI tract, the barotrauma can occur to the external auditory canal, includes teeth, the portion of the face under a face mask, and skin trapped under a wrinkle in a dry suit. The body is relatively unaware of this change in pressure.īarotrauma can potentially involve any area with entrapment of gas in a closed space. When a diver submerges, the force of the tremendous weight of the water above is exerted over the entire body. The body behaves as a liquid and follows Pascal’s law pressure applied to any part of a fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid. The pressure change with increasing depth is linear, although the greatest relative change in pressure per unit of depth change occurs nearest the surface, where it doubles in the first 33 feet of sea water. As a diver descends underwater, absolute pressure increases much faster than in air. Pressure contributes either directly or indirectly to the majority of serious diving-related medical problems.
#Treatment for pulmonary barotrauma free
When diving deep, free divers are exposed to increased pressure, causing a spectrum of injuries to the body. Divers face a unique set of underwater hazards in addition to the general aquatic problems such as drowning, hypothermia, water-borne infectious diseases, and interactions with hazardous marine life. Unlike SCUBA diving, breath-hold divers do not use supplemental air underwater. Our patient and his friends were freediving, or breath-hold diving. Spearfishing may be done while freediving, snorkeling or SCUBA diving. He was discharged home on hospital day #2. The patient remained hemodynamically stable and without respiratory distress throughout his hospitalization. Given the patient’s chest pain and subjective shortness of breath, a chest x-ray was performed.

The patient had no further hemoptysis after arrival to the emergency department. On exam, he was comfortable and his lungs were clear to auscultation bilaterally. He did not complain of any headache, visual changes, ear pain, nausea, joint or muscle pain, or any other symptoms. On arrival to the emergency department, the patient was breathing comfortably on room air. After returning to his boat, the patient was still experiencing cough, pleuritic chest pain, and mild shortness of breath. After feeling a bit better, he went down again to a depth of 30 feet in order to catch a large fish. After getting onto the boat, the patient coughed up approximately 5 tablespoons of bright red blood. On the way to the surface, he developed chest pain. The patient had dove to a depth of 50 feet using 11 lbs of weights on his belt, holding his breath along the way. The patient had been spearfishing when his symptoms began. read more ).A 24-year-old male presented to the Emergency Department with cough and hemoptysis. It can affect the ear (causing ear pain, hearing loss, and/or vestibular symptoms) or the sinuses.

Overpressurization in the sphenoid sinus occasionally compresses the optic nerve, causing decreased vision or blindness ( 3, 4 General references Barotrauma is tissue injury caused by a pressure-related change in body compartment gas volume. Maxillary sinus overpressurization can compress the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve, causing hyperesthesia over the cheek. Pain can be severe, sometimes accompanied by facial tenderness on palpation. Divers experience mild pressure to severe pain, with a feeling of congestion in the involved sinus compartments during ascent or descent and sometimes epistaxis.

Sinus barotrauma most often affects the frontal sinuses, followed by the ethmoid and maxillary sinuses ( 3 General references Barotrauma is tissue injury caused by a pressure-related change in body compartment gas volume. Weakness of both upper and lower face distinguishes facial baroparesis from stroke or arterial gas embolism ( 1 General references Barotrauma is tissue injury caused by a pressure-related change in body compartment gas volume. When pressure within the middle ear remains elevated during or after ascent from a dive, the facial nerve can be compressed (facial baroparesis), resulting in ipsilateral upper and lower facial paresis. On examination of the ear canal, the tympanic membrane may show congestion, hemotympanum, perforation, or lack of mobility during air insufflation with a pneumatic otoscope conductive hearing loss is usually present.
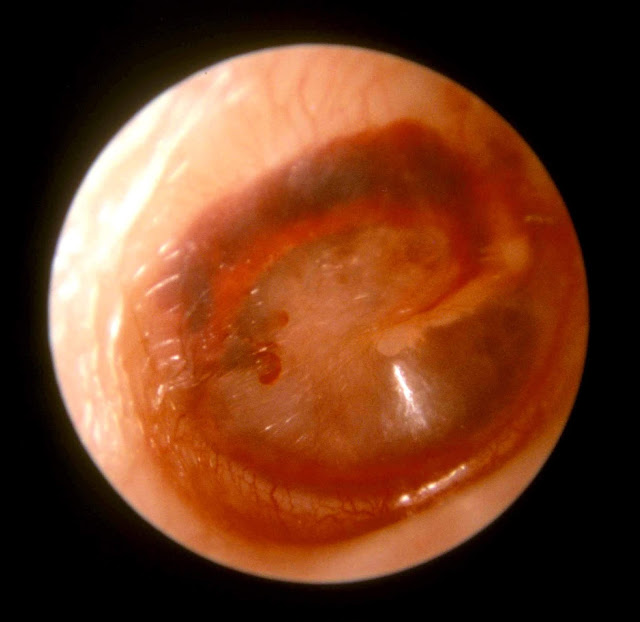
Inflow of cold water to the middle ear may result in vertigo, nausea, and disorientation while submerged. Typically, divers experience ear fullness and pain during descent if pressure is not quickly equilibrated, middle ear hemorrhage or tympanic membrane rupture may occur. Diving can affect the external, middle, and inner ear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
